Step 0 - Introduction
Step 0.1 - Principles of Doppler ultrasound
Step 0.2 - Basic physiology of the abdominal blood vessels
Step 0.2.1 - Signs and symptoms of abdominal vascular disease
Step 1 - Preparation
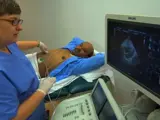
Step 1.1 - Equipment preparation
Step 1.2 - Patient preparation
Step 1.3 - Operator preparation
Step 2 - Expose the abdomen and apply gel
Step 3 - Select the transducer and obtain images of the abdominal blood vessels
Step 4 - Commence the scanning protocol for the abdominal blood vessels
Step 4.1 - Patient position
Step 4.2 - Scan plane
Step 4.3 - Images required
Step 4.4 - Annotations required
Step 4.5 - Sonographic features of normal abdominal vessels
Step 4.5.1 - Sonographic features of the normal abdominal aorta
Step 4.5.2 - Sonographic features of the normal celiac axis
Step 4.5.3 - Sonographic features of the normal common hepatic artery
Step 4.5.4 - Sonographic features of the normal splenic artery
Step 4.5.5 - Sonographic features of the normal superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
Step 4.5.6 - Sonographic features of the normal renal arteries
Step 4.5.7 - Sonographic features of the normal inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
Step 4.5.8 - Sonographic features of the normal inferior vena cava (IVC)
Step 4.5.9 - Sonographic features of the normal renal veins
Step 4.5.10 - Sonographic features of the normal superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
Step 4.5.11 - Sonographic features of the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV)
Step 4.5.12 - Sonographic features of the splenic vein
Step 4.5.13 - Sonographic features of the normal portal vein
Step 4.6 - Variants
Step 4.7 - Troubleshooting
Step 5 - Scan the aorta
Step 5.1 - Scan the proximal aorta in the longitudinal plane
Step 5.2 - Scan the mid aorta in the longitudinal plane
Step 5.3 - Scan the distal aorta in the longitudinal plane
Step 5.4 - With the patient in the supine position scan the aorta in the transverse plane
Step 5.5 - Obtain a Doppler spectral trace of the aorta
Step 5.6 - Scan celiac artery in the longitudinal plane
Step 5.7 - Scan the celiac artery in the transverse plane
Step 5.8 - Pathology of the celiac axis
Step 5.9 - Scan the SMA in the longitudinal plane
Step 5.10 - Scan the SMA in the transverse plane
Step 5.11 - Pathology of the SMA
Step 6 - Scan the inferior vena cava
Step 6.1 - Scan the proximal inferior vena cava (IVC) in the longitudinal plane
Step 6.2 - Scan the distal inferior vena cava (IVC) in the longitudinal plane
Step 6.3 - Scan the inferior vena cava (IVC) in the transverse plane
Step 6.4 - Obtain a Doppler spectral trace of the inferior vena cava
Step 7 - Scan the portal venous system
Step 7.1 - Obtain longitudinal images of the main portal vein (MPV)
Step 7.2 - Obtain a Doppler spectral trace of main portal vein (MPV)
Step 7.3 - Obtain longitudinal images of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
Step 7.4 - Obtain a Doppler trace of the SMV
Step 7.5 - Obtain a longitudinal image of the splenic vein
Step 7.6 - Obtain a Doppler trace of the splenic vein
Step 7.7 - Obtain a longitudinal image of the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV)
Step 7.8 - Obtain a Doppler trace of the IMV
Step 8 - Complete the procedure